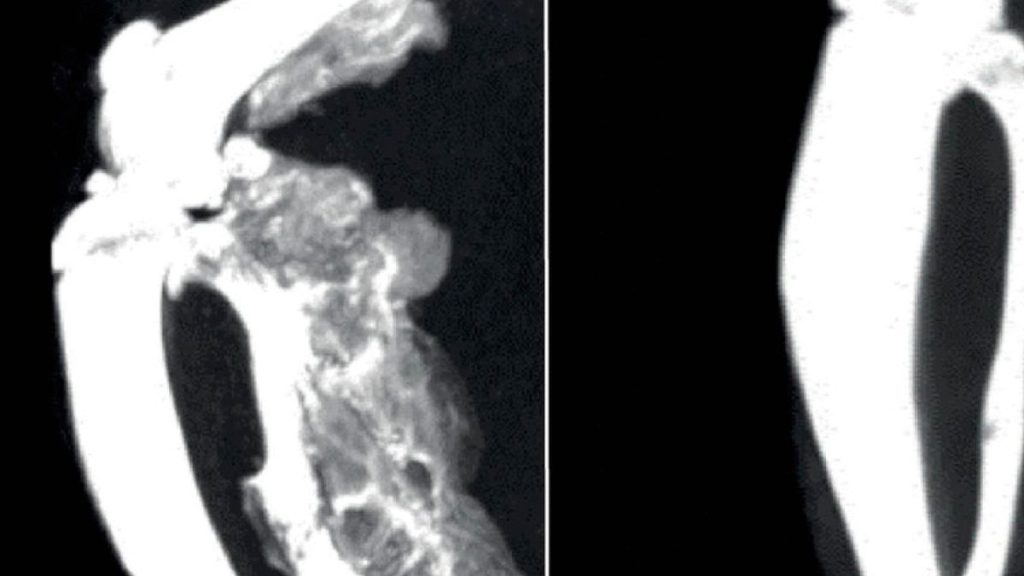
Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva (FOP) is a rare genetic disease driven by gain-of-function variants in activin receptor-like kinase 2 (ALK2), the most common variant being ALK2R206H . In FOP, ALK2 variants display increased and dysregulated signaling through the bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) pathway resulting in progressive and permanent replacement of skeletal muscle and connective tissues with […]
All posts tagged: BLU-782
BLU-782
Search
Categories
- Awareness Activities 29
- FOP Trust Activities 17
- INDIA News 20
- International 23
- Medicine Updates 26
- Patient Stories 22
- Uncategorized 57
Recent Posts
-
 A Week of Preventive Treatment and Emergency Flare-Up Management
A Week of Preventive Treatment and Emergency Flare-Up Management -
 Mayeshree’s Journey — Staying Ahead of Future Flare-Ups
Mayeshree’s Journey — Staying Ahead of Future Flare-Ups -
 Coordinating Hospitals and Doctors Across India for Seamless FOP Care
Coordinating Hospitals and Doctors Across India for Seamless FOP Care -
 FOP Awareness Expands — Training Program Held for Police Personnel
FOP Awareness Expands — Training Program Held for Police Personnel -
 Global Guidelines Continue to Shape Local Treatment Decisions
Global Guidelines Continue to Shape Local Treatment Decisions
Tags
Abnormal Bone (1)
Actionable Disease (1)
ALK2 Inhibitor (1)
Bedside-to-Bench (1)
BLU-782 (1)
Blueprint’s (1)
Bone Growth Disease (1)
case (1)
Cellular (1)
Children (16)
comfortable sleeping position (1)
Creative (4)
CureFOP (1)
Disease (1)
Drug (1)
Drug Trial (1)
FDA (1)
Fibrodysplasia Ossificans (1)
Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva (38)
FOP (20)
Genetic Mutation (1)
Genome-Editing Method (1)
Heterotopic Ossification (7)
IFOPA (15)
Internet (2)
Mobile (6)
Molecular (1)
Nutrition (2)
Ongoing Clinical Trials (1)
Orphan Drug (1)
oxidative phosphorylation (1)
parents (1)
Phase 2 LUMINA-1 (1)
Pipeline Report (1)
potential treatment (1)
Preimplantation Genetic Testing (1)
Rare Disease (1)
Rare ‘Catastrophic’ (1)
Research (2)
Shelter (2)
Startup (4)
support (1)
Tissue Turns to Bone. Treatment (1)
Tori of Nigerian (1)
Underpuppy (1)